
Air Exhaust Heat Pumps
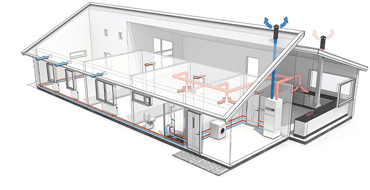
Air exhaust heat pumps extract the air from a ductwork system which is connected to the warm areas of the building. Heat is removed from the air and transferred into the heat pump circuit where the heat pump then raises the temperature of the refrigerant and transfers this heat into the domestic hot water system. It also provides heat to the house via under floor heating (the ideal) or radiator heat emitters.
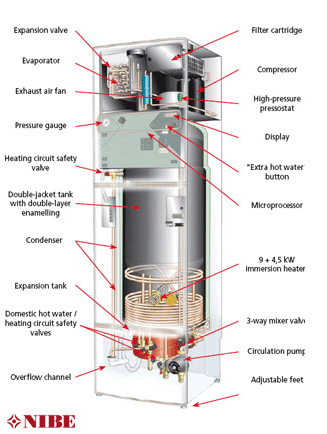
The efficiency of a heat pump is measured in Coefficient of Performance (CoP). A CoP of 3 means that for every 1Kw of energy put into the heat pump you would get 3kw of energy output. This would be in the form of warm water to the heating system with flow temperatures of between 35°C and 45°C which is much lower than a conventional domestic boiler.
Exhaust heat pump units can generate higher temperatures but this would reduce the CoP of the unit and providing less economic benefit to the householder. The lower the operating temperature of the system provides the maximum system efficiency.
Air exhaust heat pumps should cover the heating requirements of a well insulated property and when used in conjunction with a cylinder immersion heater both the heating and hot water needs should be met. The immersion heater raises the temperature of the domestic hot water when required.



